What is Supernova?
A supernova is the biggest explosion that humans have ever seen. Each blast is the extremely bright, super-powerful explosion of a star.
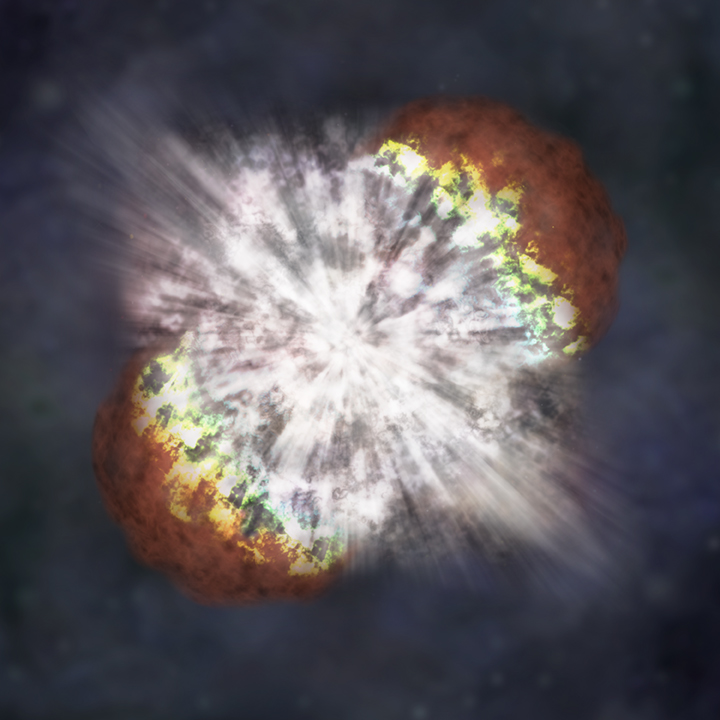

An illustration of one of the brightest and most energetic supernova explosions ever recorded.
What causes a supernova?
One type of supernova is caused by the “last hurrah” of a dying massive star. This happens when a star at least five times the mass of our sun goes out with a fantastic bang!
Massive stars burn huge amounts of nuclear fuel at their cores, or centers. This produces tons of energy, so the center gets very hot. Heat generates pressure, and the pressure created by a star’s nuclear burning also keeps that star from collapsing.
A star is in balance between two opposite forces. The star’s gravity tries to squeeze the star into the smallest, tightest ball possible. But the nuclear fuel burning in the star’s core creates strong outward pressure. This outward push resists the inward squeeze of gravity.
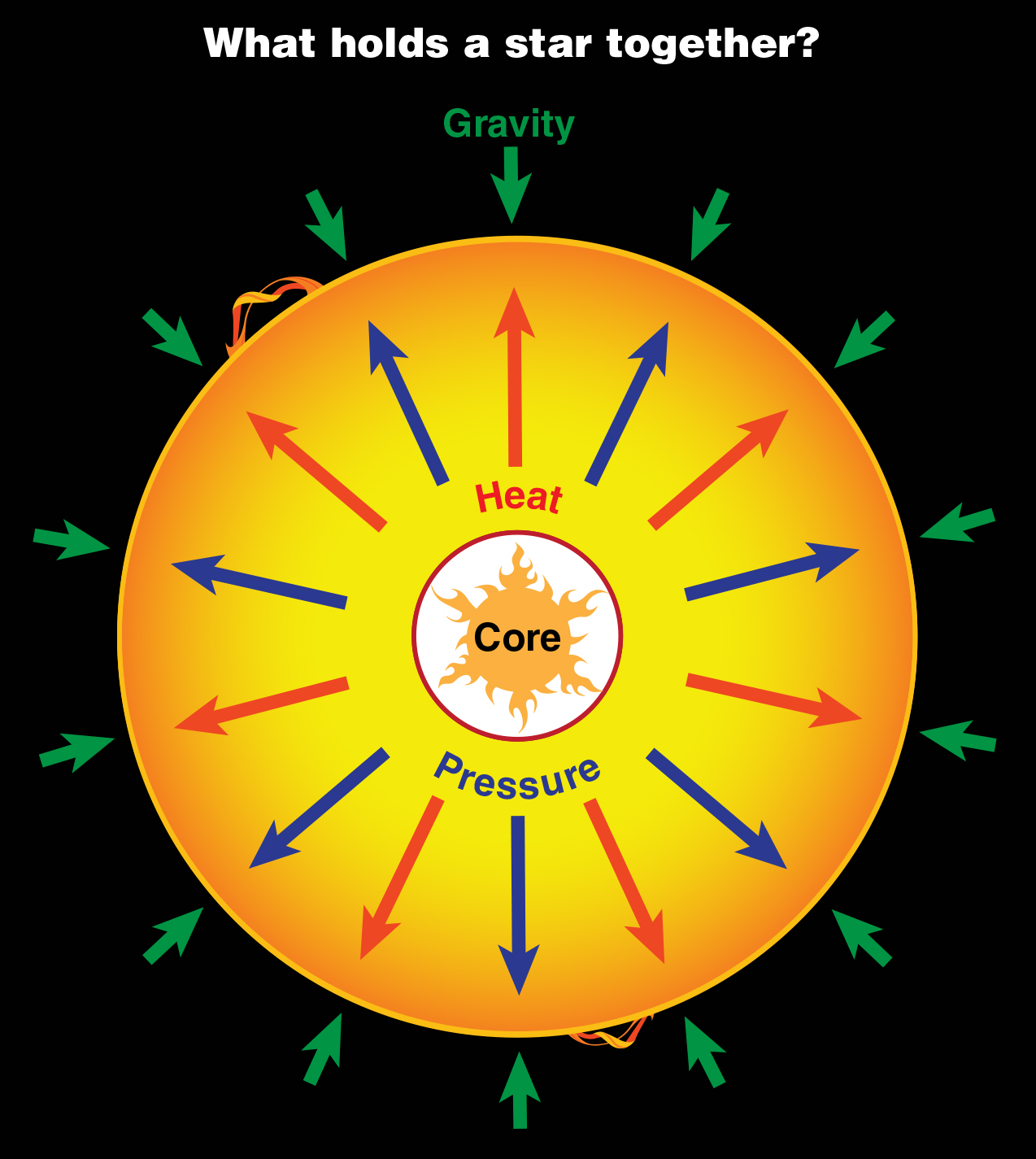
What holds stars together? It’s a balance of gravity pushing in on the star and heat and pressure pushing outward from the star’s core.
When a massive star runs out of fuel, it cools off. This causes the pressure to drop. Gravity wins out, and the star suddenly collapses. Imagine something one million times the mass of Earth collapsing in 15 seconds! The collapse happens so quickly that it creates enormous shock waves that cause the outer part of the star to explode!
Usually a very dense core is left behind, along with an expanding cloud of hot gas called a nebula. A supernova of a star more than about 10 times the size of our sun may leave behind the densest objects in the universe—black holes.

The Crab Nebula is the leftover, or remnant, of a massive star in our Milky Way that died 6,500 light-years away. Astronomers and careful observers saw the supernova in the year 1054.
A second type of supernova can happen in systems where two stars orbit one another and at least one of those stars is an Earth-sized white dwarf. A white dwarf is what's left after a star the size of our sun has run out of fuel. If one white dwarf collides with another or pulls too much matter from its nearby star, the white dwarf can explode. Kaboom!
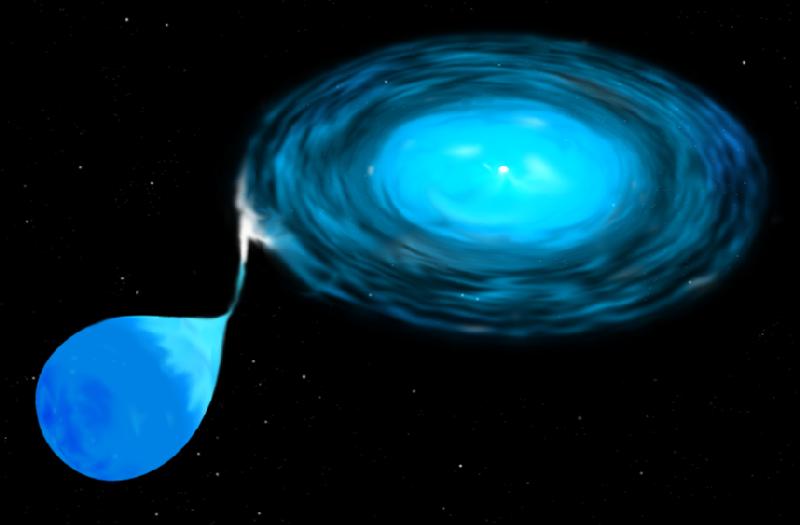

In this illustration, a white dwarf pulls matter from a companion star. Eventually, this will cause the white dwarf to explode.
Comments
Post a Comment